It’s critical that medical laboratory leaders prepare for increased scrutiny and pressure from DOJ fraud investigations
Recent efforts by federal investigators to ferret out and prosecute healthcare fraud have shown that certain clinical laboratory companies are guilty of fraud and abuse. And as Dark Daily covered in “Preparing Clinical Laboratories for Invasive Federal Enforcement of Fraud and Abuse Laws, Increased Scrutiny by Private Payers, New Education Audits, and More,” November 13, 2019, the US Department of Justice (DOJ) and other federal and state regulators are becoming more aggressive in their hunt for bad actors.
Thus, clinical laboratory leaders must constantly be on guard against being drawn into potentially fraudulent activities. For example, schemes involving substance-use disorder (SUD), which are the latest healthcare-related scams to draw the attention of the DOJ.
Lack of Oversight in Substance-Use Disorder (SUD) Leads to Fraud
According to four experts who co-authored a blog post in Health Affairs, America’s opioid epidemic has affected more than 20 million lives and become a “hot spot” for healthcare fraud.
“Substance-use disorder (SUD) treatment was a $9 billion per year industry in 1986 and is now a $35 billion industry that is expected to reach $42 billion in 2020,” they wrote. Thus, it has given rise to escalating opioid-related scams by unethical clinical laboratories, healthcare providers, and recovery-house operators.
Anuradha Rao-Patel, Lead Medical Director Government Programs at Blue Cross and Blue Shield of North Carolina; Michael Adelberg, Principal and Healthcare Strategy Lead at Faegre Baker Daniels Consulting; Samantha Arsenault, Vice President of National Treatment Quality Initiatives at Shatterproof; and Andrew Kessler, JD, Founder and Principal of Slingshot Solutions, explained in Health Affairs how lack of oversight led to the increase in fraud.
“While current regulations around SUD treatment aim to protect patient safety instead of criminalize addiction treatment, they vary by state—and in some states, patient protections are limited,” they explained. “This lack of oversight invites deceptive business practices, insurance fraud, patient neglect, and ultimately, treatment malpractice that can damage lives and tear families apart.”
In December 2019, the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office of the Inspector General (OIG) released its Semiannual Report to Congress. The report details the $5.9 billion HHS recovered from healthcare fraud investigations during fiscal year 2019, more than double the amount of the prior year.
Included in that amount was a $17 million settlement with Acadia Healthcare (NASDAQ:ACHC), and its subsidiary, CRC Health, LLC, which allegedly defrauded Medicaid out of $8.5 million from 2012 to 2018. According to a DOJ press release, the clinical laboratory testing reimbursement scheme ended in the largest healthcare fraud settlement in West Virginia history.

The Health Affairs authors focused on the major players in addiction treatment-related fraud that were highlighted in a 2018 Government Accountability Office (GAO) report. They are:
- SUD treatment providers who take advantage of “gaps in regulations and quality assurance to offer substandard and fraudulent care that endangers patients and wastes money.”
- Unlicensed patient brokers who SUD providers pay to transport addicts to them, often from hundreds of miles away.
- Disreputable recovery house or “sober home” operators who are subsidized financially by fraudulent SUD providers.
One example the GAO report outlined involved SUD providers in Florida who funded their illegal operations by billing patients’ insurance hundreds of thousands of dollars in unnecessary drug testing over the course of several months.
“At the very moment that ethical healthcare providers are working harder than ever to address the opioid crisis, unethical actors—such as providers engaged in fraud—pose a growing problem,” the Health Affairs authors stated.
Opioid Crisis Turns Urine Screening into ‘Liquid Gold’
Kaiser Health News (KHN) reported that many doctors who prescribe opioids began making drug screenings routine in their practices after being persuaded that doing so would keep them in good standing with licensing boards and law enforcement, while also reducing their liability and preventing patient abuse of prescription pills.
In some instances, doctors opened their own clinical laboratories, KHN stated.
KHN described the nation’s painkiller addiction as turning urine screening into “liquid gold,” particularly for doctors who operate their own clinical laboratories. In 2014 and 2015, Medicare paid $1 million or more for drug-related tests billed by healthcare workers at more than 50 pain management practices in the US, KHN reported.
“It was almost a license to steal. You had such a lucrative possibility, it was tempting to sell as many [tests] as you can,” Charles Root, PhD, Senior Consultant at consulting firm CodeMap, told KHN. CodeMap provides publications, tools, and services that help healthcare professionals navigate the federal Medicare program and has tracked the increase in medical testing laboratories in doctors’ offices, KHN noted.
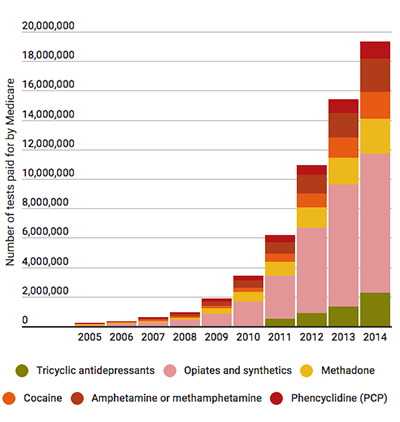
Federal officials have taken notice of physicians whose priority is testing patients, not treating them. Jason Mehta, JD, who at that time was Assistant US Attorney in Jacksonville, Fla., told KHN, “We’re focused on the fact that many physicians are making more money on testing than treating patients. It is troubling to see providers test everyone for every class of drugs every time they come in.”
Clinical laboratories have an important role to play in identifying fraud and solving the opioid epidemic. Not only are lab leaders ideally positioned to help providers better understand drug test ordering and interpretation, but also to help develop value-based interventions within the continuum of care for this national health crisis.
—Andrea Downing Peck
Related Information:
United States Attorney Announces $17 Million Healthcare Fraud Settlement
Liquid Gold: Pain Doctors Soak Up Profits by Screening Urine for Drugs



