Under-resourced British healthcare system faces a record high backlog of care with 5.61 million people in England waiting for hospital-based medical procedures
Healthcare in the United Kingdom (UK) is about to become much more expensive. The UK government has announced plans to substantially increase payroll taxes to fund the surging demand for care due to the COVID-19 pandemic. But that may only be the part of the healthcare-funding iceberg visible above the surface. Below the surface is a healthcare system where wait times for access to many types of care—including cancer diagnoses—are already unacceptable.
Some pathologists and medical laboratory executives in the US who have long questioned healthcare reformers’ desire to introduce an NHS-like single-payer healthcare system in this country will not be surprised to learn that the UK’s notoriously underfunded National Health Service (NHS) is facing a record waitlist for hospital-based medical diagnostic tests and procedures.
Consequently, Reuters reported, the high cost of fighting the COVID-19 pandemic has pushed British Prime Minister Boris Johnson into breaking with election promises and announcing plans to raise payroll taxes to record levels so that more money can be funneled into the struggling government-run healthcare system.

Speaking to lawmakers in the House of Commons, British Prime Minister Boris Johnson (above) acknowledged his tax plan breaks his Conservative Party’s election year pledge to not raise VAT (value-added tax), income, or national insurance taxes. He insists that the COVID-19 pandemic created unprecedented challenges for the national health system. “I accept that this breaks a manifesto commitment, which is not something I do lightly, but a global pandemic was in no one’s manifesto,” he told lawmakers, Reuters reported. (Photo copyright: The Independent.)
5.6M People on Growing NHS Waiting List for Treatments and Procedures
When the COVID-19 pandemic struck the UK in March 2020, the NHS suspended elective surgeries such as hip or knee replacements and cataract removal and postponed many patients’ medical laboratory diagnostic tests.
In “Record 5.6M People in England Waiting for Hospital Treatment,” The Guardian estimated that 1.4 million patients were added to the waiting lists during the pandemic’s first 18 months. More than one-third of the 5.6 million people waiting for care in July 2021 had been on a waitlist for at least 18 months, the paper noted. Since then, the waiting list has grown by 150,000 people per month, as more people who did not seek or could not access NHS treatments during the pandemic returned to their doctors’ offices.
Johnson’s tax hike formula for fixing the record NHS backlog and improving social care for the elderly created shockwaves in the UK’s Conservative Party, which, like the Republican Party in this country, has championed low taxes. But Johnson maintains the government is out of options.
“It would be wrong for me to say that we can pay for this recovery without taking the difficult but responsible decisions about how we finance it,” Johnson told Parliament. “It would be irresponsible to meet the costs from higher borrowing and higher debt,” he added.
But Johnson’s proposal drew the wrath of some members of his own party and provided the opposition Labor Party with ammunition to denounce the prime minister’s leadership during the pandemic.
In “U.K. Is Among First Western Nations to Increase Taxes to Cover COVID-19 Costs,” The Wall Street Journal (WSJ) reported that Labor Party leader Keir Starmer compared Johnson’s tax increases to putting a bandage “on gaping wounds that his party inflicted,” and questioned why they weren’t levied more directly on the rich. The UK government says the wealthiest 14% will pay about half of the extra tax revenues, the WSJ noted.
“This is a tax rise that breaks a promise that the prime minister made at the last election … Read my lips, the Tories can never again claim to be the party of low tax,” Starmer told Reuters.
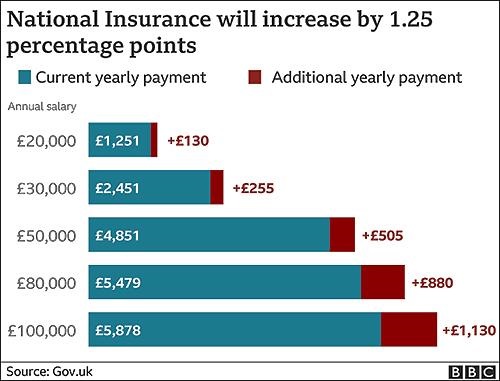
The BBC graphic above illustrates how the tax hikes, which were approved by the Parliament on September 8 by a 319 to 248 vote, will increase the national insurance payroll tax paid by workers and employers by 1.25% each. CNBC reported that the UK government projects the increased taxes will raise £36 billion (US$49.6 billion) over the next three years. (Graphic copyright: BBC.)
Politics versus Hard Facts
According to The Guardian, in 2023-2024, national insurance contributions will be rebranded as a health and social care levy, with more of the money raised going to social care. The added funding will enable the UK government to implement a new cap on total care costs so that no individual will pay more than £86,000 (US$117,142) over their lifetime for social-care programs. Currently, many seniors are forced to sell their homes to meet unexpected care costs, the newspaper noted.
In “Britain’s Tax Warning to America,” the WSJ editorial board criticized Johnson’s plan as a “new middle-class entitlement.”
“One message to voters and investors is that taxes are set to rise for years to come,” the WSJ editorial board wrote, predicting the cost of social care will escalate as the UK’s population ages, and that the planned diversion of future taxes for social care will be presented as a “cut” in NHS funding. They maintained that the danger in Johnson’s decision goes deeper than breaking an election campaign pledge or nationalizing more of the UK’s healthcare economy.
“The larger problem is that national healthcare and other entitlements become ever more unaffordable even as they are politically impossible to reform,” the newspaper stated. “The Tories are becoming tax collectors for the entitlement state, which is deadly for parties of the right.”
Bloomberg noted that the UK Institute for Fiscal Studies predicts the planned April 1 tax increase will “raise the UK tax burden to its highest-ever sustained level since records began in 1955—about 35% of national income.”
But, according to the UK-based The Health Foundation, at £2,646.95 (US$3,648.43) per person in 2019, the United Kingdom spends less on healthcare than many developed countries. Less per person than the:
- US (£6,782.80),
- Germany (£4,131.21),
- France (£3,307.54),
- Japan (£2,949.19) and
- Canada (£2,823.07).
And when healthcare costs are viewed as a percentage of a country’s gross domestic product (GDP), the UK (8% GDP) lags behind the US (13.9%), Germany (9.9%), Japan (9.3%) and France (9.3%) and exceeds only Canada (7.6%) and Italy (6.4%).
While US hospitals, healthcare systems, and patients continue to struggle with ever-increasing healthcare costs, reformers who promote a single-payer healthcare system as an answer to this nation’s healthcare ills may want to take a hard look at the outcomes of the UK’s model.
Clinical laboratory managers and pathologists interested in how the US healthcare system can be improved might be well-served to study the experience of the National Health Service in the UK, that, like all other health systems in the world, has its own unique methods for how it serves its population.
—Andrea Downing Peck
Related Information:
U.K. Is Among First Western Nations to Increases Taxes to Cover Covid-19 Costs
Britain’s Tax Warning to America
Taxes and Healthcare Funding: How Does the UK Compare?
Record 5.6M People in England Waiting for Hospital Treatment
UK PM Johnson Raises Taxes to Tackle Health and Social Care Crisis
UK’s Boris Johnson to Hike Taxes to Tackle Covid and Social-Care Crises
Johnson Wins Healthcare Vote to Push UK Taxes to Highest Ever



Trackbacks/Pingbacks