Research could lead to improvements in gene therapy and antiviral resistance medications while also possibly leading to a new class of clinical laboratory tests
Scientists at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC) have discovered what may be the scariest virus of all—the Vampire Virus. It’s a term that may inspire “Walking Dead” level horror in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, and though virologists and microbiologists might be tempted to dismiss them as imaginary, they are all too real. Even more apropos to the Dracula saga, the UM scientists found them in a soil sample. Yikes!
Happily, this ghoulish discovery could have positive implications for gene editing, gene therapy, and the development of new antiviral medications, according to The Conversation. In turn, these positive implications may eventually trigger the need to create new diagnostic tests that clinical laboratories can offer to physicians.
The UMBC scientists published their findings in the journal ISME, a publication of the International Society for Microbial Ecology, titled, “Simultaneous Entry as an Adaptation to Virulence in a Novel Satellite-Helper System Infecting Streptomyces Species.”
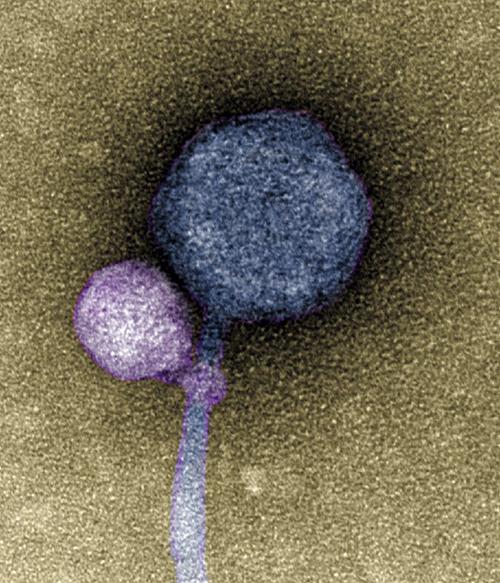
The image above, taken from a University of Maryland news release, shows the satellite virus “latched onto its helper virus.” Discovery of vampire-like viruses that attach at the “neck” of other viruses may lead to important discoveries in the development of gene editing and antiviral therapies. Might clinical laboratories one day collect samples for pharmaceutical developers engaged in combating antiviral drug resistance? (Photo copyright: University of Maryland.)
Spotting a Vampire Virus
According to IFLScience, these tiny vampire viruses were first discovered by undergraduates who believed they were looking at sample contamination when analyzing sequences of bacteriophages from environmental soil samples. But upon repeating the experiment they realized it was no mistake.
In the UMBC news release, bioinformatician Ivan Erill, PhD, Professor of Biological Sciences at the University of Maryland, noted that “some viruses, called satellites, depend not only on their host organism to complete their life cycle, but also on another virus, known as a helper.
“The satellite virus needs the helper either to build its capsid, a protective shell that encloses the virus’ genetic material, or to help it replicate its DNA,” he added. “These viral relationships require the satellite and the helper to be in proximity to each other at least temporarily, but there were no known cases of a satellite actually attaching itself to a helper—until now.”
Although scientists have witnessed viruses working together before, this is the first known instance of a virus directly latching onto another virus’ capsid—rather like a vampire going for the neck.
“When I saw it, I was like, I can’t believe this,” said Tagide deCarvalho, PhD, Assistant Director of Natural and Mathematical Sciences at the University of Maryland and first author of the study, in a UM news release, “No one has ever seen a bacteriophage—or any other virus—attach to another virus.”
Visualizing the tiny viruses was only possible through the use of the transmission electron microscope (TEM) at UMBC’s Keith R. Porter Imaging Facility (KPIF), to which deCarvalho had access.
“Not everyone has a TEM at their disposal. [With the TEM] I’m able to follow up on some of these observations and validate them with imaging. There’s elements of discovery we can only make using the TEM,” said deCarvalho in the UMBC news release.
Using Vampire Viruses to Develop Better Gene Therapies
Spookily, the comparisons to Dracula and his parasitic brethren do not stop with their freeloading tendencies. The researchers found that some viruses without a satellite attached still showed signs of having been leeched onto before. Those viruses had the equivalent of “bite marks” showing evidence of encountering vampiric viruses in the past.
“It’s possible that a lot of the bacteriophages that people thought were contaminated were actually these satellite-helper systems,” said deCarvalho in the ISME paper.
But what does UMBC’s breakthrough mean for the greater scientific and medical community? Do we need to arm host viruses with silver crosses and necklaces of garlic? Jokes aside, this discovery could lead to further development in research of how to genetically alter viruses and deliver therapeutic elements into cells.
According to Healthline, some gene therapy or “gene editing” already involves the use of viruses. Scientists switch out the programming on a virus and trick it into healing, instead of harming the cells it infiltrates. Therefore, UMBC’s discovery could lead to new breakthroughs battling deadly viruses by using their own parasitic tricks to infiltrate other viruses.
Although groundbreaking and extremely interesting, the research is still in early stages. Any developments from this discovery aren’t likely to impact clinical laboratories any time soon. But after the past few years of battling the COVID-19 variants, this exciting discovery could help find new ways to prevent the next pandemic.
—Ashley Croce
Related Information:
Virus Seen Latching onto Another Virus (Like A Tiny Vampire) for First Time
UMBC Team Makes First-Ever Observation of a Virus Attaching to Another Virus
The First Discovered Vampire Virus Hooks Onto other Viruses—Meet the ‘MiniFlayer’
Your Guide to Gene Therapy: How It Works and What It Treats
Bizarre First: Viruses Seen ‘Biting’ onto Other Viruses Like Tiny Vampires


