New Wearable In-Ear Medical Device Helps Sufferers of Standing-Related Ailments
Device is latest example that wearable healthcare devices are moving past simple biomarker monitoring and into the area of assisting in rehab
Companies unrelated to traditional clinical laboratory medicine continue to develop wearable devices that enable individuals to monitor their health while also alerting physicians and caregivers in real time when certain biomarkers are out of range.
One recent example is US biotechnology company STAT Health Informatics in Boston, which has developed a wearable device that monitors blood flow to the ear and face “to better understand symptoms such as dizziness, brain fog, headaches, fainting, and fatigue that occur upon standing,” according to a press release. The tiny device is worn in the ear and connects wirelessly to a smartphone app.
Johns Hopkins University clinically tested the STAT device, and according to Medical Device Network, “It can predict a person fainting minutes before it happens and can be worn with more than 90% of devices that go in or around the ear. It can also be left in while sleeping and showering, meaning less likelihood of removing the device and forgetting to replace it.”
Another notable aspect of this invention is that it’s an example of how the ongoing miniaturization of various technologies makes it possible to invent smaller devices but with greater capabilities. In the case of the STAT device, it combines tiny sensors, Bluetooth, and an equally tiny battery to produce a device that fits in the ear and can function for up to three days before needing a recharge.
It’s easy to imagine these technologies being used for other types of diagnostic testing devices that could be managed by clinical laboratories.
Johns Hopkins published its findings in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology: Clinical Electrophysiology titled, “Monitoring Carotid Blood Flow Using In-Ear Wearable Device During Tilt-Table Testing.”

“It’s well understood that the ear is a biometric gold mine because of its close proximity to the brain and major arteries. This allows for new biometrics … to be possible,” said Daniel Lee (above), co-founder and CEO of STAT Health, in a press release. “In addition, the ear is largely isolated from data corruption caused by arm motion—a problem that plagues current wearables and prevents them from monitoring heart metrics during many daily tasks. The ear is really the ideal window into the brain and heart.” Clinical laboratory managers may want to watch how this technology is further developed to incorporate other biomarkers for diseases and health conditions. (Photo copyright: STAT Health.)
How STAT Works
Every time the wearer stands, the STAT device tracks the change in response of blood pressure, heart rate, and blood flow to the head. “The device distills all this information into an ‘Up Score’ to track time spent upright. Its ‘Flow Score’ helps users pace their recovery by watching for blood flow abnormalities,” MassDevice reported.
According to the company’s website, STAT is intended for use in individuals who have been diagnosed with conditions known to suffer from drops in blood flow to the head, such as:
- Dysautonomia,
- POTS [postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome],
- OH [orthostatic hypotension],
- Long COVID, and
- ME/CFS [chronic fatigue syndrome].
As an individual continues to use the device, STAT “learns about each user’s unique body to provide personalized coaching for healthy lifestyle choices,” MassDevice reported.
Another key factor is the technology built into the device. An optical sensor was chosen over ultrasound because STAT Health felt it was both easy to use and provided precise measurements accessing the shallow ear artery, MassDevice reported.
“Despite its small scale, the device incorporates advanced optical sensors, an accelerometer, a pressure sensor, temperature sensors, artificial intelligence (AI)-edge computing, three-day battery life (or more), and a micro solar panel,” Medical Device Network noted.
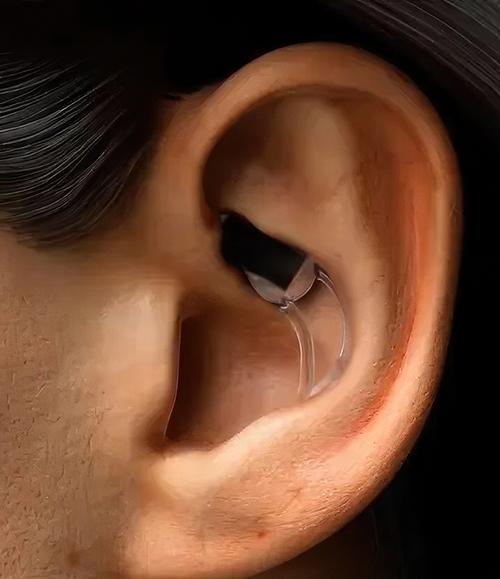
STAT’s image above demonstrates how truly minute the company’s wearable device is, even though it monitors blood flow to the face and ear looking for signs that the wearer is about to suffer bouts of dizziness or lightheadedness due to a drop in blood flow. (Photo copyright: STAT Health Informatics Inc.)
STAT’s Impact on Users’ Health
STAT’s developers intend the device to help individuals stay on track with their health. “The target population can navigate their condition better. If they’re not standing when they can, they will become deconditioned. This product encourages standing and being upright where possible, as part of rehab,” Lee told Medical Device Network.
Lee has been developing wearable in-ear devices for many years.
“Nobody has realized the ear’s true potential due to the miniaturization and complex systems design needed to make a practical and user-friendly ear wearable,” he told MassDevice. “After multiple engineering breakthroughs, we’ve succeeded in unlocking the ear to combine the convenience and long-term nature of wearables with the high fidelity nature of obtrusive clinical monitors. No other device comes close along the axis of wearability and cardiac signal quality, which is why we believe STAT is truly the world’s most advanced wearable.”
For clinical laboratories, though STAT is not a diagnostic test, it is the latest example of how companies are developing wearable monitoring devices intended to allow individuals to monitor their health. It moves beyond the simple monitoring of Apple Watch and Fitbit. This device can aid individuals during rehab.
Wearable healthcare devices will continue to be introduced that are smaller, allow more precise measurements of target biomarkers, and alert wearers in real time when those markers are out of range. Keeping in tune with the newest developments will help clinical laboratories and pathologists find new ways to support healthcare providers who recommend these devices for monitoring their patients conditions.
—Kristin Althea O’Connor
Related Information:
Monitoring Carotid Blood Flow Using In-Ear Wearable Device During Tilt-Table Testing
STAT Health Launches First In-Ear Wearable to Measure Blood Flow
Stat Health Launches In-Ear Wearable That Measures Blood Flow



